In the realm of healthcare, understanding and effectively documenting symptoms and diagnoses is paramount. One common ailment that healthcare professionals frequently encounter is right lower quadrant (RLQ) pain. Furthermore, This article will delve into the world of ICD-10 codes for RLQ pain, shed light on its various causes, and also explore effective treatment strategies to alleviate this discomfort.
What is Right Lower Quadrant Pain
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ) pain is the term used to describe discomfort or pain experienced on the lower right side of the abdomen. It is a widespread symptom with numerous potential causes, from minor digestive problems to potentially fatal illnesses like appendicitis. Moreover, For healthcare professionals to effectively record and treat patients’ illnesses, they must be familiar with the ICD-10 codes for RLQ pain.
Importance of Proper Coding
Properly coding RLQ pain is essential for medical records, insurance claims, and accurate patient care. The correct ICD-10 code ensures that healthcare professionals can identify the underlying cause of the pain and administer appropriate treatment promptly.
What are ICD-10 Codes?
ICD-10 codes, short for the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Edition, are alphanumeric codes used by healthcare providers to classify and document medical diagnoses and procedures. Moreover, These codes help streamline communication among healthcare professionals and insurance providers, ensuring accurate billing and effective patient care.
The Significance of ICD-10 Codes in Healthcare
ICD-10 codes act as a common language in the medical field. They make it simpler for healthcare professionals to choose the best treatment options and track health trends on a larger scale by enabling them to properly identify and describe a patient’s condition.
ICD-10 Codes for RLQ Pain
ICD-10 Code K58.0: Irritable Bowel Syndrome
One common cause of RLQ pain is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). ICD-10 code K58.0 is used to classify this condition. IBS often leads to abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements, making it a prevalent source of discomfort in the RLQ.
ICD-10 Code K59.00: Constipation
Constipation, coded as K59.00, can cause significant RLQ pain. Moreover, It occurs when stool moves slowly through the colon, leading to abdominal discomfort, and can be a result of various factors such as dietary choices, dehydration, or medication side effects.
ICD-10 Code R10.31: Lower Abdominal Pain
R10.31 is a general code used for lower abdominal pain. While it doesn’t specify RLQ pain, it can be indicative of various RLQ issues, including those discussed here.
ICD-10 Code K65.9: Peritonitis, Unspecified
Peritonitis, often characterized by RLQ pain, is represented by ICD-10 code K65.9. Furthermore, This condition involves inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane lining the abdominal cavity.
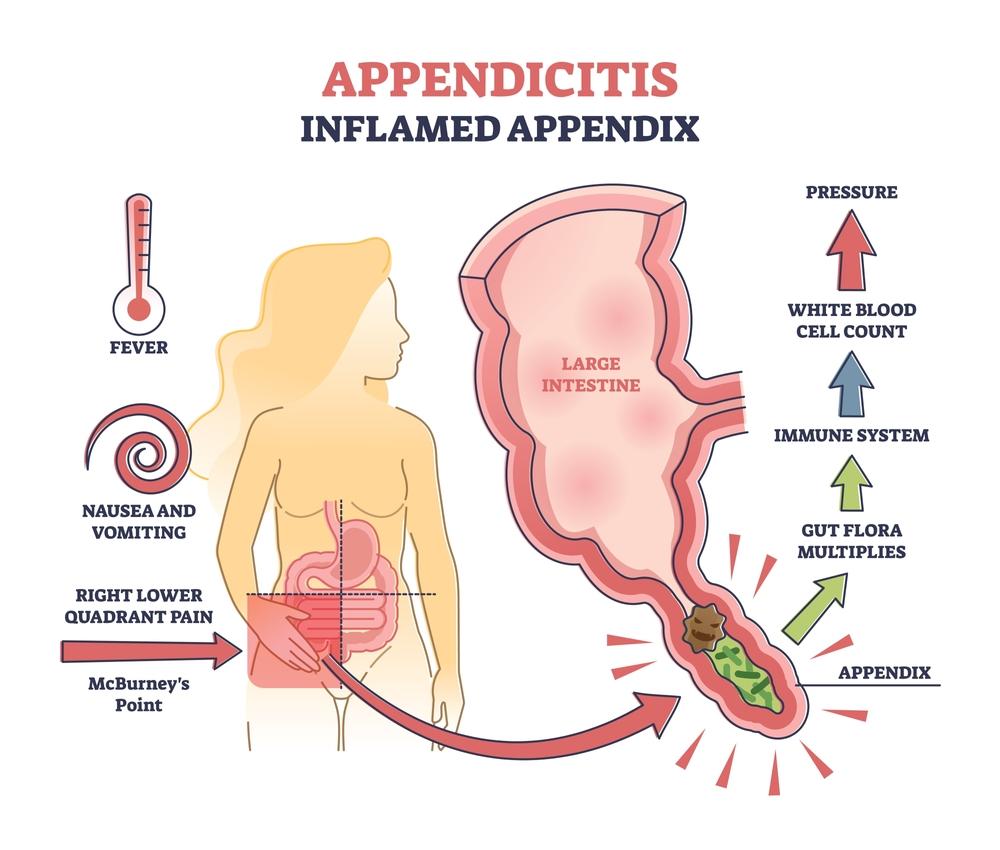
ICD-10 Code K35.80: Acute Appendicitis
ICD-10 code K35.80 designates acute appendicitis, a condition that could be dangerous. The possibility of an appendix rupture necessitates rapid medical intervention.
Common Causes of RLQ Pain
Appendicitis
Appendicitis, often diagnosed with ICD-10 code K35.80, is a severe medical condition that manifests as RLQ pain. If left untreated, it can lead to a burst appendix, which is life-threatening.
Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis of the large intestine, without perforation or abscess and without bleeding, is assigned the ICD-10 code K57.30. Moreover, It’s essential to differentiate between diverticulosis and diverticulitis, as the latter may require more aggressive treatment.
Gastrological Disorders
Various gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease or diverticulitis, can cause RLQ pain due to inflammation or obstruction in the intestines.

Urological Conditions
Furthermore, Certain urological conditions, including kidney stones, can cause referred pain to the RLQ, making it crucial to consider urological evaluations in RLQ pain cases
Gynecological Issues
In females, gynecological problems like ovarian cysts or endometriosis can lead to RLQ pain, often necessitating specialized care and diagnosis.
Musculoskeletal Problems
Musculoskeletal issues, such as muscle strains or hernias in the abdominal wall, can mimic RLQ pain and require appropriate examination and diagnosis.
Diagnostic Approaches
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional is often the first step in diagnosing RLQ pain. Moreover, Palpation, auscultation, and assessment of vital signs help identify potential causes.
Laboratory Tests
Furthermore, Blood tests, urinalysis, and fecal tests may be ordered to check for infection, inflammation, or other underlying conditions contributing to RLQ pain.
Imaging Studies
The abdominal region can be visualized in great detail using imaging investigations like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI, which can help diagnose structural abnormalities.
Treatment Strategies
Conservative Management
For less severe cases, conservative management involves dietary modifications, pain management, and lifestyle changes to alleviate RLQ pain.
Appendicitis Management
For patients diagnosed with acute appendicitis, surgical removal of the inflamed appendix is the standard treatment. This procedure, known as an appendectomy, is typically performed laparoscopically, resulting in a shorter recovery period.
Diverticulosis Care
Treatment for diverticulosis often involves dietary changes, including increased fiber intake, to prevent complications. If diverticulitis occurs (infection or inflammation of the diverticula), antibiotics and, in severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Surgical Intervention
In cases of acute appendicitis or other surgical emergencies, prompt surgical intervention is necessary to remove the affected appendix or address other issues causing RLQ pain. Appendectomy, hernia repair, and diverticulitis resection are common surgical procedures.
Medications
Moreover, Medications may be prescribed to manage pain, control inflammation, or address specific underlying conditions contributing to RLQ pain. For example:
- Diverticulitis or appendicitis antibiotics.
- IBS-related discomfort relief using antispasmodic medications.
- Painkillers for a variety of uncomfortable ailments.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes, such as dietary adjustments and stress management, can also be effective in reducing RLQ pain associated with conditions like IBS.
Living with RLQ Pain
Coping Mechanisms
Living with chronic RLQ pain can be challenging. Coping mechanisms, such as support groups and relaxation techniques, can help individuals manage their discomfort effectively.
Support Networks
Building a support network with friends, family, and healthcare providers is essential for individuals dealing with RLQ pain. Additionally, It provides emotional and practical assistance throughout the journey.
Final Thoughts
In the world of healthcare, understanding and addressing RLQ pain is of utmost importance. Properly coding RLQ pain using ICD-10 classifications ensures accurate documentation and timely treatment. Moreover, With the right diagnosis and treatment strategies, individuals experiencing RLQ pain can find relief and improve their quality of life.
Why choose Zee Medical Billing?
Unlock the power of precision with ZEE Medical Billing! Our expert team ensures accurate medical billing documentation and coding, paving the way for smoother operations and increased revenue for your practice. Trust us to handle the complexity while you focus on providing top-notch care to your patients. Experience the ZEE difference today!
Frequently Asked Questions
RLQ pain can be caused by various conditions, some of which require immediate medical attention, while others can be managed conservatively. In addition, It’s crucial to seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause.
Home remedies like applying a warm compress and maintaining a healthy diet can help alleviate mild RLQ pain. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for persistent or severe pain.
Yes, RLQ pain can sometimes be associated with ectopic pregnancies or other pregnancy-related complications. Moreover, If you suspect pregnancy and experience RLQ pain, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Preventive measures for RLQ pain may include maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and managing stress. However, the effectiveness of prevention varies depending on the underlying cause.
The lower right side of the abdomen is often the site of RLQ pain. A medical expert must be consulted for a correct diagnosis and to distinguish this condition from other stomach problems.